"Delving into the realm of private health insurance for self-employed business owners sheds light on a crucial aspect of financial planning and well-being. Let's explore the intricacies and benefits that come with this specialized coverage."
Overview of Private Health Insurance for Self-Employed Business Owners
Private health insurance for self-employed individuals refers to health insurance coverage that is purchased directly by individuals who are self-employed or own a business. Unlike traditional employer-sponsored health insurance plans, self-employed individuals are responsible for selecting and paying for their own health insurance coverage.Having private health insurance is crucial for self-employed business owners as it provides them with access to quality healthcare services without having to rely on employer-provided benefits.
It offers a sense of security and peace of mind knowing that they have coverage for medical expenses in case of illness or injury.
Benefits of Private Health Insurance for Self-Employed Business Owners
- Customizable Coverage: Self-employed individuals can tailor their health insurance plans to suit their specific needs and budget. They have the flexibility to choose the level of coverage, deductibles, and copayments that work best for them.
- Access to a Wide Network of Providers: Private health insurance often offers a broader network of healthcare providers, giving self-employed business owners more options for choosing doctors, specialists, and hospitals.
- Timely Medical Care: With private health insurance, self-employed individuals can receive timely medical care without long wait times typically associated with public healthcare systems.
- Health and Wellness Programs: Many private health insurance plans offer additional benefits such as wellness programs, preventive care services, and access to telemedicine, promoting overall health and well-being.
- Financial Protection: Private health insurance provides financial protection against high medical costs, ensuring that self-employed business owners are not burdened with exorbitant healthcare expenses.
Types of Private Health Insurance Plans Available
When it comes to private health insurance plans for self-employed business owners, there are several options to consider based on individual needs and preferences.
Individual Health Plans vs. Group Health Plans
Individual health plans are purchased by individuals or families directly from an insurance provider, offering customized coverage based on personal requirements. On the other hand, group health plans are typically offered by employers to their employees, pooling together a large group to negotiate better rates and benefits.
Self-employed individuals can sometimes join group health plans through professional organizations or industry associations.
Key Features of High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs)
High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) are a popular choice for self-employed individuals due to their lower monthly premiums and the option to contribute to a Health Savings Account (HSA). These plans come with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs, but they offer lower premiums and the opportunity to save money tax-free for medical expenses.
HDHPs are suitable for those who are generally healthy and want to save on monthly premiums while still having coverage for major medical expenses.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Health Insurance Plan

When selecting a private health insurance plan as a self-employed business owner, there are several crucial factors to take into account to ensure you have the coverage you need without breaking the bank.
Coverage Options
- Consider the specific healthcare services and treatments that are covered by the plan. Make sure it includes the essential services you require, such as doctor visits, hospital stays, prescription drugs, and preventive care.
- Look for additional benefits like mental health services, maternity care, or specialist consultations if you anticipate needing them.
Deductibles, Premiums, and Out-of-Pocket Costs
- Assess the deductible amount you will need to pay out of pocket before the insurance starts covering costs. A higher deductible usually means lower monthly premiums, but you'll have to pay more upfront for services.
- Compare premiums across different plans to find a balance between affordability and coverage. Keep in mind that lower premiums might come with higher deductibles and out-of-pocket costs.
- Calculate your potential out-of-pocket expenses, including copayments and coinsurance, to estimate the total cost of the plan over a year.
Network Coverage and Access to Healthcare Providers
- Check if your preferred doctors, specialists, hospitals, and healthcare facilities are part of the plan's network. Out-of-network care can be significantly more expensive or may not be covered at all.
- Consider the flexibility of the plan in allowing you to see healthcare providers outside the network if you have specific preferences or need specialized care.
- Evaluate the quality of care provided by the network providers to ensure you receive high-standard medical services when needed.
Tax Implications and Deductions Related to Private Health Insurance
As a self-employed business owner, understanding the tax implications and deductions related to private health insurance is crucial for managing your finances effectively. By being aware of how you can deduct health insurance premiums from your taxes, you can make informed decisions when purchasing a private health insurance plan.
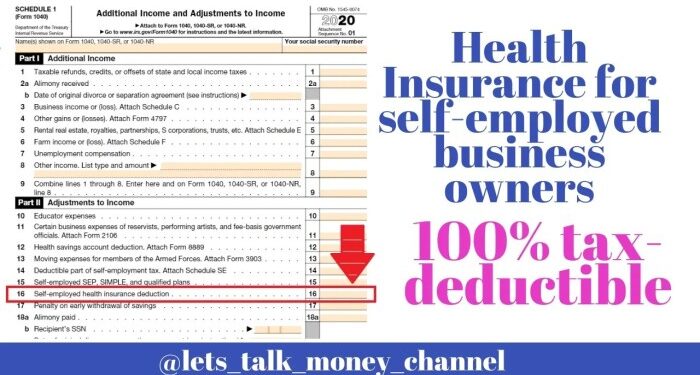
Deducting Health Insurance Premiums
Self-employed individuals have the advantage of deducting health insurance premiums from their taxes as an adjustment to income. This means that you can reduce your taxable income by the amount you pay for health insurance, resulting in lower tax liability.
Eligibility Criteria for Claiming Deductions
- To be eligible for claiming health insurance deductions, you must be self-employed and not eligible for an employer-sponsored health plan.
- Your health insurance policy must be established under your business, and you cannot be eligible to participate in a subsidized health plan.
- You can claim deductions for health insurance premiums paid for yourself, your spouse, your dependents, and your children under the age of 27.
Benefits of Tax Deductions for Self-Employed Individuals
By deducting health insurance premiums from your taxes, self-employed individuals can lower their taxable income, resulting in reduced tax liability. This can lead to significant savings and better financial management for your business.
Last Recap
"In conclusion, navigating the landscape of private health insurance for self-employed business owners requires careful consideration and understanding. By weighing the options and implications, individuals can make informed decisions to safeguard their health and finances effectively."
Helpful Answers
"Is private health insurance more expensive for self-employed individuals compared to traditional employment-based plans?"
"Private health insurance for self-employed individuals can be more expensive due to lack of employer contributions, but the flexibility and tailored coverage often outweigh the costs."
"Can self-employed business owners qualify for subsidies or tax credits to help with private health insurance costs?"
"Self-employed individuals may be eligible for subsidies or tax credits based on their income level and family size. It's advisable to explore these options to reduce financial burdens."
"How does private health insurance affect the ability to see specific healthcare providers?"
"Private health insurance plans may have networks of preferred providers, impacting the choice of healthcare professionals. It's essential to check network coverage to ensure access to desired providers."